Yoast WordPress SEO Tutorial, Set up SEO in an Optimal Way
Yoast WordPress SEO Tutorial v3
 Getting the best WordPress SEO settings in WordPress can be handled by a number of different plugins, one of the more popular ones is WordPress SEO from Yoast (1 million active WordPress installs). Recently it has been upgraded to version 3 which is a major rewrite of the codebase on how the plugin functions. The upgrade has been a bit shaky with six incremental updates to address the bugs – however the plugin still delivers its core purpose.
Getting the best WordPress SEO settings in WordPress can be handled by a number of different plugins, one of the more popular ones is WordPress SEO from Yoast (1 million active WordPress installs). Recently it has been upgraded to version 3 which is a major rewrite of the codebase on how the plugin functions. The upgrade has been a bit shaky with six incremental updates to address the bugs – however the plugin still delivers its core purpose.
This tutorial covers the WordPress SEO plugin by Joost De Valk, it is a powerhouse of a tool that deals with all the SEO configurables you could ever think of for a WordPress installation. The plugin is robust and can be optimally tuned for search engine results. The plugin has had a major upgrade to version 3 and this guide has been updated to reflect it.
If you already have an existing WordPress SEO plugin but want to change to the Yoast one you can swap to it by using a plugin called ‘SEO Data Transporter‘ which can migrate data from SEO plugins such as Headspace, Platinum and All in One SEO. It is always best just to use the one SEO plugin.
If you do migrate from another plugin, do the migration to the Yoast WordPress SEO Plugin with the SEO Data Transporter and then disable the older SEO plugin.
Another option is that if you are using Headspace2 or All-In-One SEO you can use the import option of the Yoast WordPress SEO plugin directly.
This guide aims to go through the different Yoast WordPress SEO settings and give the user explanations and some good settings as a baseline on what to use, obviously everyones needs are different so don’t feel like your settings have to match exactly what is in the guide, there are no best settings as such and people will argue on what works better.
I have updated the information as of December 2015. The guide is quite lengthy and broken up into various parts, I have added scroll backs to the 2 main lists in the text so you can easily return to the listed tabs.
Installation & Activation
In WordPress go to ‘Plugins’ > ‘Add New’ type in ‘WordPress SEO’ and ‘Install Now’ and then activate it.
Interface Settings
Once activated the plugin is accessible from the WordPress Dashboard in both the horizontal menu and the vertical sidebar, the horizontal menu has a couple of links to keyword research tools including the Google Keyword Tool, Google Insights and a link to Aaron Wall’s SEO Book keyword tool – the links below are to the WordPress SEO settings which are the same as the ones lower down to the left in the vertical sidebar.
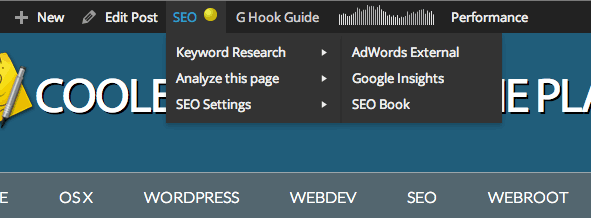
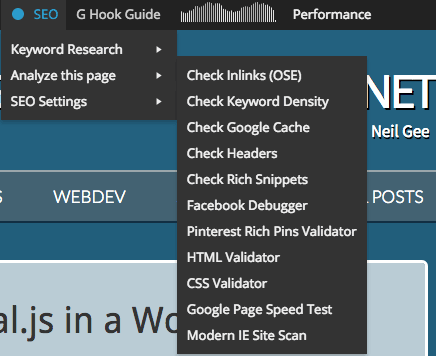
In the ‘Analyse this page‘ link you can check on your incoming links to the page via OpenSite Explorer which is a Moz (SEOMoz) tool, check your keyword density via Zippy, check whats in Googles cache or simply get a HTTP header response of the current page via a Joost de Valk app.
More recent features of the Page Analysis as well as the Google Rich Snippets and Facebook Debugger links, are HTML and CSS validation as well as Pinterest validation, IE scan and Google page speed test, all of these services copy the URL you are on and run the page through the corresponding service, very handy.
Also lately added is a mobile friendly test, which will run through the page and give you feedback if the page is mobile friendly.
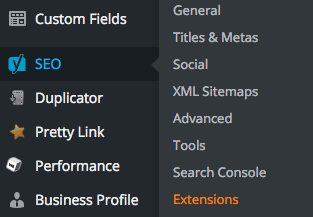
Most of the same settings as in the SEO Settings horizontal menu are also stacked in the WordPress Dashboard sidebar under ‘SEO’ are:
In the newer version there is the Search Console that allows you to access your Google WebMaster Tools, Search Console data.
The Yoast SEO plugin works from 2 levels; global and local settings.
Global settings are sitewide and include default SEO settings for all your content, where as local settings are more granular and specific to posts, pages and categories.
WordPress SEO Global Settings
- General
- Titles & Meta
- Social
- XML Sitemaps
- Permalinks
- Breadcrumbs
- RSS
- Import & Export
- Bulk Title and Description Editor
- Edit Files
- Extensions
- Search Console
- Local SEO Box
The settings listed above are more of a global configuration for SEO in your WordPress blog – there is also a local SEO Box setting per post/page/category/tag level configuration, which can override the global settings this is explained at the bottom of the post (click the above ‘Local SEO Box’ link above to get to the local per page/post settings).
But first we will look at the overall global settings…
General
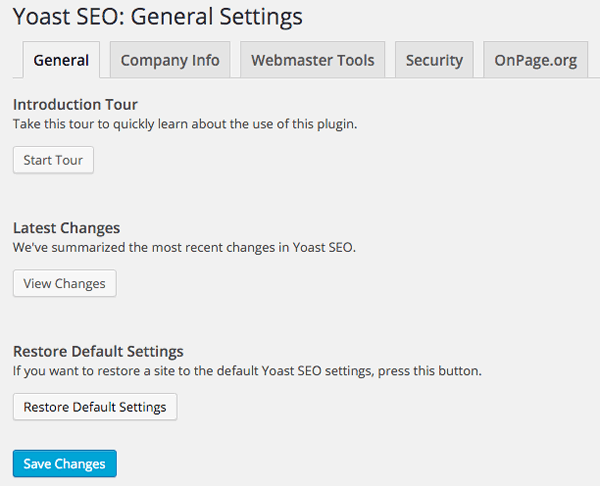
The General settings has a good introduction to the plugin via the “Start Tour” button.
There is also a link to the latest changes in the plugin summarized in the WordPress dashboard.
There is also an option here to restore to the default settings.
At the top of the General box are 4 additional tabs;
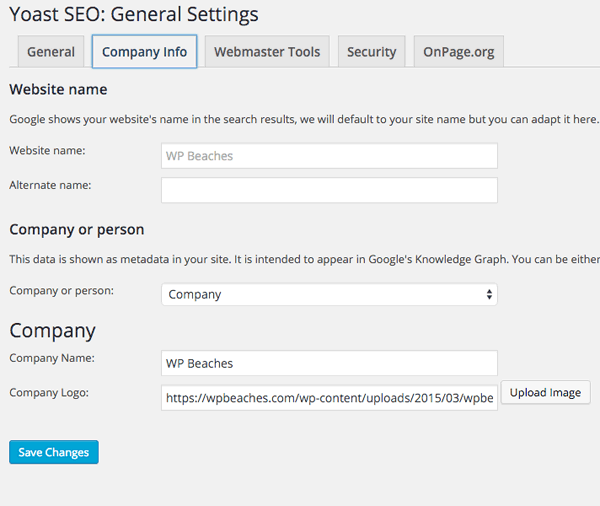
Your Info
Declare whether the site is about a company or person and upload a company logo – this is for Google’s Knowledge Graph. This is sometimes displayed if someone does a search on your company name.
Webmaster Tools
– like it says either leave if already verified with these search engines or enter your sites details.
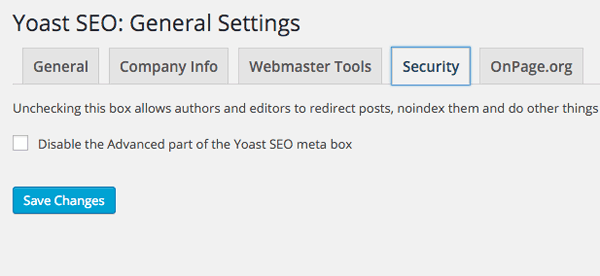
Security
If you run a multi author site you may want to restrict editors and authors from using certain options of the plugin, otherwise just leave it unchecked.
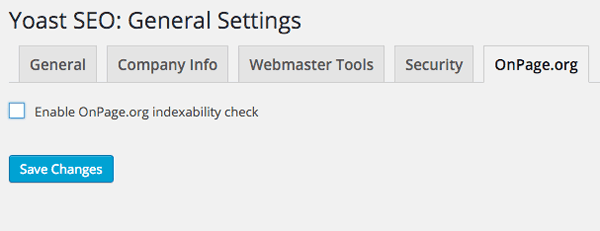
OnPage.org
A new feature here is the ability to disable a check that displays an alert saying that your web page is not indexed. This alert would appear in a WordPress style message in the dashboard and would be incorrect in the early versions of the version3 plugin.
The OnPage.org service offers a technical SEO suite, this looks like a partnership between Yoast and OnPage – you can check your sites index via Google Webmaster Tools, now known as the Search Console or run a simple search in your browser using this format
site:yourdomain.com
Titles & Meta
The next section “Titles & Meta” is divided into 6 tabs across the top.
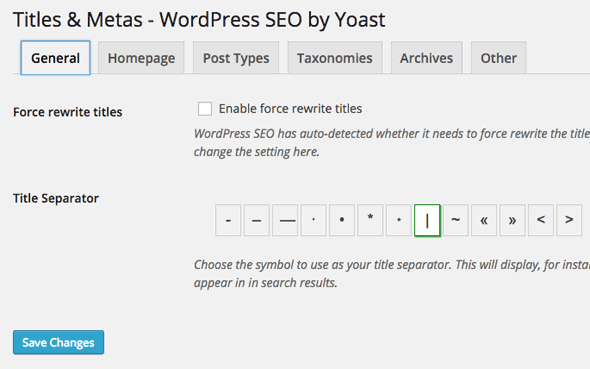
Tab1 – General
Title Settings
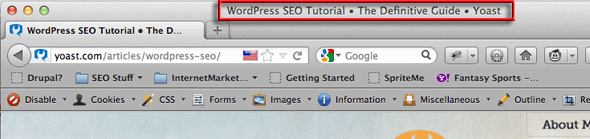
Titles is probably the most important factor in on-page SEO; the Title Tag. The title is hidden in the head of a html document as a meta tag but displayed in some browsers in the title at the top, example here is in Firefox.
Search Engines will record this meta tag and give value to its importance of what keywords are used in it – typically it should not exceed 70 characters and should have a natural flow and be relevant to the content of the page – so do not stuff it full of keywords.
Force Rewrite Titles
The ‘title’ should be published exactly as you write one in the Title field (set globally and locally) and published in the head of the document, some WordPress themes however have their own code which interferes with what you want. There are 2 ways to make sure you get the titles you want; one is a check box that forces the title to re-write and the other is making sure a snippet of PHP code is pasted into the ‘header.php‘ of your WordPress theme header file, the latter resulting in a faster more efficient process.
Copy the php function code
<?php wp_title(''); ?>
In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Appearance > Editor locate your header.php file and paste in the code replacing the existing code in between the title tags. For example Twenty Eleven theme has the below code in between its title tags:
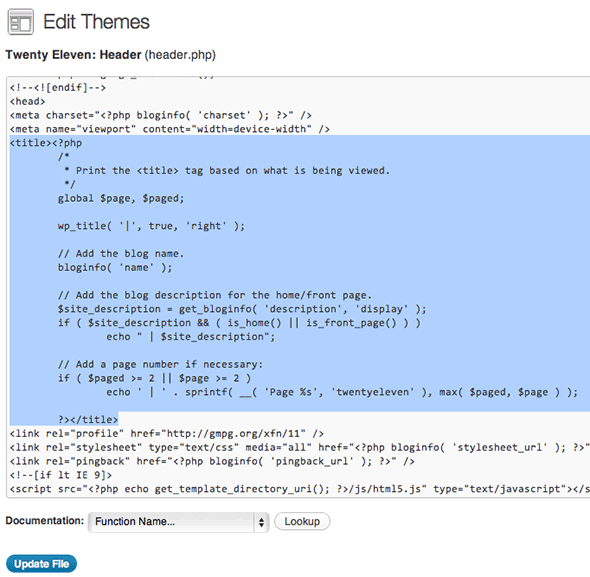
Rewrite SEO Title Tags in header
Just replace it with:
<title><?php wp_title(''); ?></title>
If you feel uncomfortable editing the code just check the ‘Force Rewrite Titles’ box instead.
But some themes have additional code which make the title of the blog appear twice, should this happen then you definitely need to paste in the php snippet between the title tags.
Title Separator
Pick which one suits your taste – it is applied as a word separator between distinct pieces of data in the title.
Tab2 – Home
These link to your home and blog page will take you direct to those pages and you just fill in the local Yoast WordPress SEO box fields on those pages. In some instances (depending on the theme) the links are not shown, instead you fill out the default settings on this page.
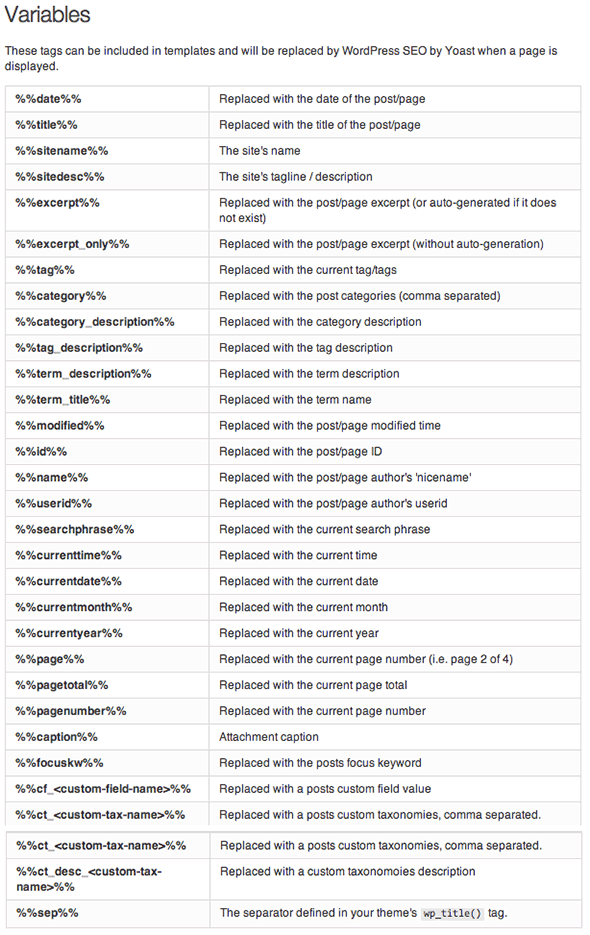
The Missing Tab – Variables
There was a sixth tab in previous versions which shows all the SEO WordPress ‘variables‘ that can be used in the global settings for all the different post types. You include all the %% symbols and the text in between. The variable is used as a placeholder in the template and swapped out for the real value for each post/page meta box.
Yoast SEO Variables
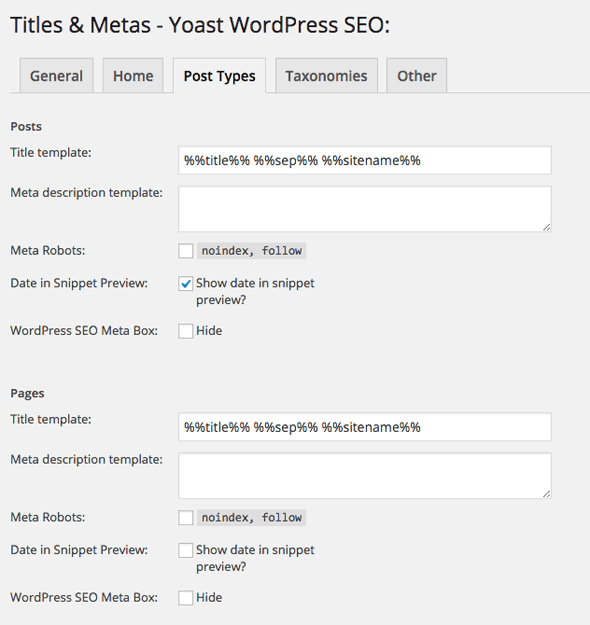
Tab3 – Post Types
This template sets up your Posts and Pages and Media/Attachment Pages and any other Custom Post Types you may have. People will have their own take on what works best here.
Using the variables in the above example – the SEO Title, %%title%% will be replaced with the Title of the post/page as entered when creating a post, then the separator %%sep%%, and then the sitename, %%sitename%%.
It’s a preference thing, so you don’t have to append the sitename, the Description will be the excerpt which is generated from the content if not explicitly set and the keywords will be set from any focus keyword set in the local SEO Box option as well as any tags set to the content, this is a good setting as you don’t have to spend any time thinking about meta keywords.
You can choose to set the content to noindex, follow if you so desired, generally though you want the content indexed in Google so leave that checkbox unchecked – at the local level you can override individual content and make that set to ‘noindex‘ which you may want to do for private pages or purposely duplicated pages.
You can chose to show the date of the post in the snippet preview which appears in the search index, if you update and publish new content on a regular basis I would leave this on as readers would see that the site is active – if your a long time in between drinks then maybe hide it.
You can hide altogether the local SEO Meta Box which would then only allow you to control the SEO settings via the global level.
You can override all these settings on a post/page individual basis by entering data directly in the local SEO box on the post/page editor level.
For custom post types you may see additional formats, these could be your themes extra post types or shopping cart product types from WooCommerce, if these types are also required to be on the search engine them ensure you also fill in values for those additional post types as well.
Tab4 – Taxonomies
Taxonomies are basically how you like to categorize your content into word terms and it comes in two forms in WordPress – Categories and Tags – generally speaking categories are broader with a hierarchal structure and more widely used, tags are more specific, of a flat structure and used to a lesser degree.
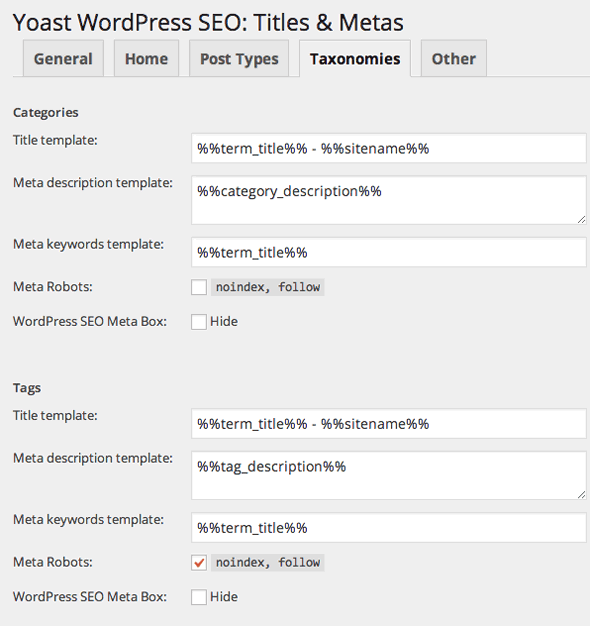
Using the above variables would be relevant for these taxonomy pages. The %%term_title%% is the actual taxonomy (the name itself of the category or tag) – I choose not to index my tags as I use categories more than tags. It’s not really wise to use the same word terms in both categories and tags as that is verging on duplicate content and also not the right way to structure your content.
Make a call on tags and categories – if you use both uniquely leave both indexed – if you use one more than another or have the same category/tag values then disable one of them. By disabling certain duplicate content you ensure that your original post/page gets the most value from the search engine and also avoid any duplicate content issues and you also make your site’s structure optimised.
Again you may see additional Taxonomy formats if you have custom taxonomies, they will also display under the Taxonomies section – apply the sane style of tags to these. These will either be introduced by themes and plugins or custom coding.
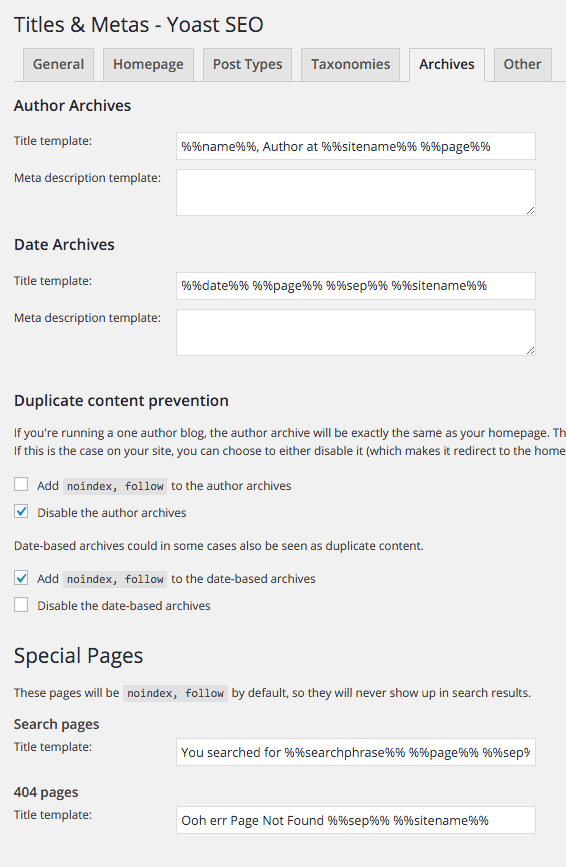
Tab 5 – Archives
Next up is the Special Pages covering Author and Date Archives and Search & 404 Pages
I think the defaults for these settings are pretty good, I have chose not to index my date archives and disable the author archives as it is a one author website I want to avoid any duplicate content in Google. For the Search & 404 pages you can add in descriptive text and the variables you need.
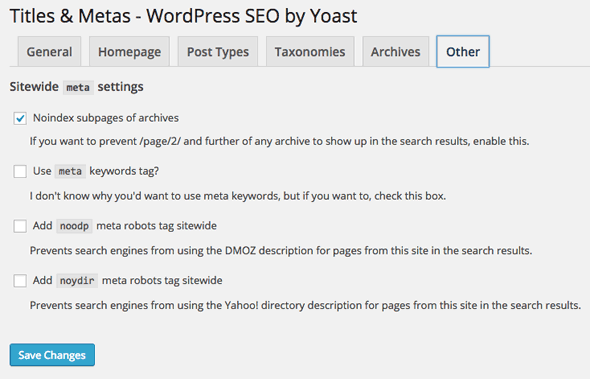
Tab 6- Other
Sitewide Meta Settings
Noindex subpages of Archives
– Check the box to prevent Google from indexing additional pages of content that are already indexed.
Use meta keywords tag?
– The keywords tag has been greatly depreciated by search engines but some pundits have declared it still has a minimal role with some engines – here my advice is to check it on but don’t spend more than a couple of minutes filling it out – this field becomes active if checked at the global level and you fill it in per post/page at the local level.
noodp & noydir
– If you have DMOZ/Yahoo directory listings for your site you will have a special meta tag for those, if you don’t want to use those meta tag description values for your site pages in the Google index then check these options. If you don’t have those listings don’t worry about it.
For the head cleaning section here it’s pretty safe to disable the top 3 but leave RSS unchecked if you want and use it.
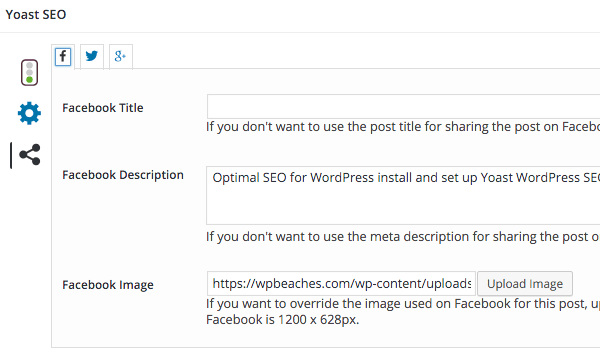
Social
With more SEO weight being put on social media signals you need to interlink your site with any available social media sites. The first tab here allows you to add in social media links for accounts that you have set up.
The Yoast SEO plugin allows you to publish facebook and twitter meta data tags in the head section of your pages, these tags can use snippets of your data for use in your Facebook links. You can also enter a Facebook admin to link back to Facebook to see your data insights
Facebook uses OpenGraph meta tags from the head of your document which allows Facebook to retrieve objects on your page and use them properly structured in Facebook pages or links posted on Facebook, you can enable these tags by checking the ‘Add OpenGraph meta data’ box.
The social settings here also allow you to specify a default image.
This image will be used if there are no images on the page/post being shared on Facebook. Otherwise an image on the post/page will be used. This also can be overridden at the local level of a post or page.
To check what og meta data is being used for your pages run the URL through the Facebook debugger tool… http://developers.facebook.com/tools/debug, you can use the link on the front end via the WP SEO menu.
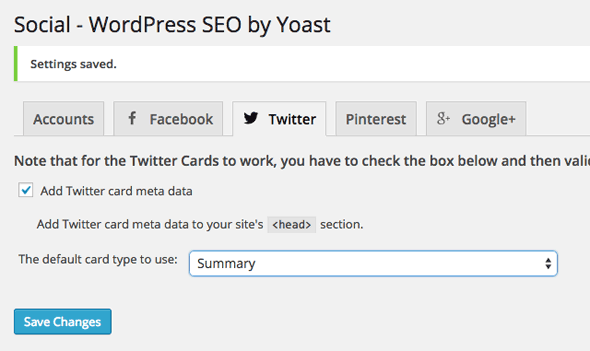
The Twitter Tab is pretty self explanatory – chose to add in a Twitter meta tag with your Twitter name.
The Google+ tab sectioned has changed in the latest version only allowing a Google+ business page onto the homepage, previously you could have both Author & Publisher. However the Author tag is now a redundant feature by Google.
To verify you have it set up correctly check via Google structured data tool.
There is also a Pinterest tab which you add in your Pinterest verification.
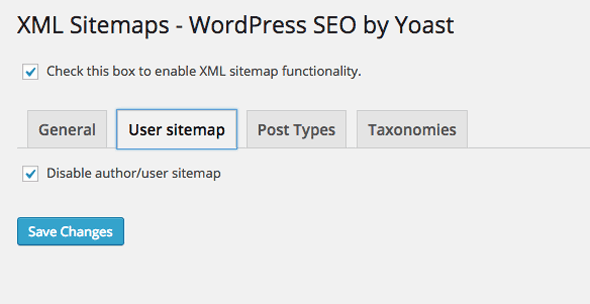
XML Sitemaps
 Click on XML Sitemap to see the actual URL string and sitemap in another window.
Click on XML Sitemap to see the actual URL string and sitemap in another window.
If you don’t use any other plugins for Sitemaps then you will want this enabled which will then give further options – the default settings are pretty much what you want; no content exclusions and all major search engines notified when new content is published.
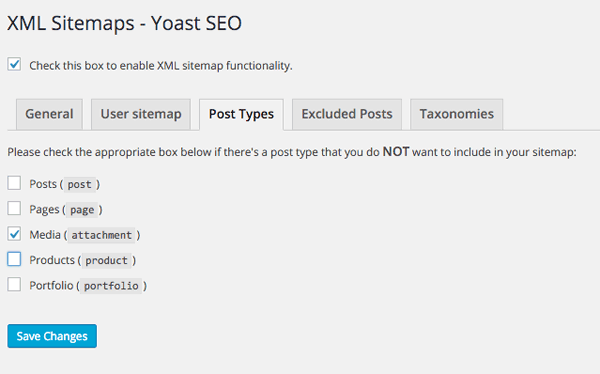
Here in the other tabs you can exclude certain content if you just want it excluded on the search index –
Custom Post Types – You may have a certain post type that you want to exclude from the search index, here I am disabling the attachment cpt for media images, I don’t want to index it.
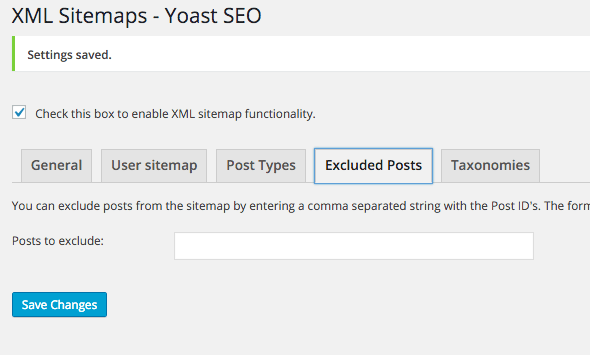
Posts – you can exclude certain posts by adding in their post-id – you can also do this at a local setting for the post.
Taxonomies – Here I do not want to include a couple of things in the sitemap as I don’t believe they will have any value to the content or there may be certain taxonomies that you simply don’t want indexed, the duplicate tag/category terms issue spring to mind if you use both you may want to disable one of them.
The master sitemap can be found at /sitemap_index.xml which has sub sitemaps to include each content type (and more if you have custom post types) –
Each time new content is added to your site the sitemaps are updated, the search engines notified of your new sitemap which in turn will get your content indexed faster and also notify you of any errors in the Webmaster tools account.
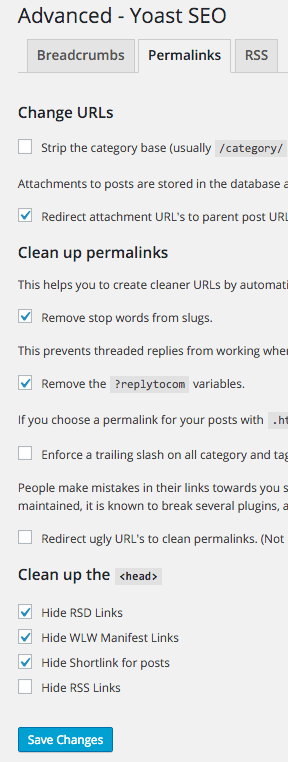
Advanced menu has three submenu items – Breadcrumbs, Permalinks and RSS
Permalinks
The defaults are fine on this – just the attachment redirected to it’s linked post page is beneficial.
I also like to remove the stop words from slugs, no benefit just a preference.
The actual permalink structure of the URLs are set in Dashboard > Settings > Permalinks, the good thing is that in the latest version of WordPress the urls are clean (no dynamic characters like ?) and the default structure uses the postname as the string in the URL.
Here you can also remove some data from the head section, I don’t really use the first 3 so I have disabled them.
Breadcrumbs
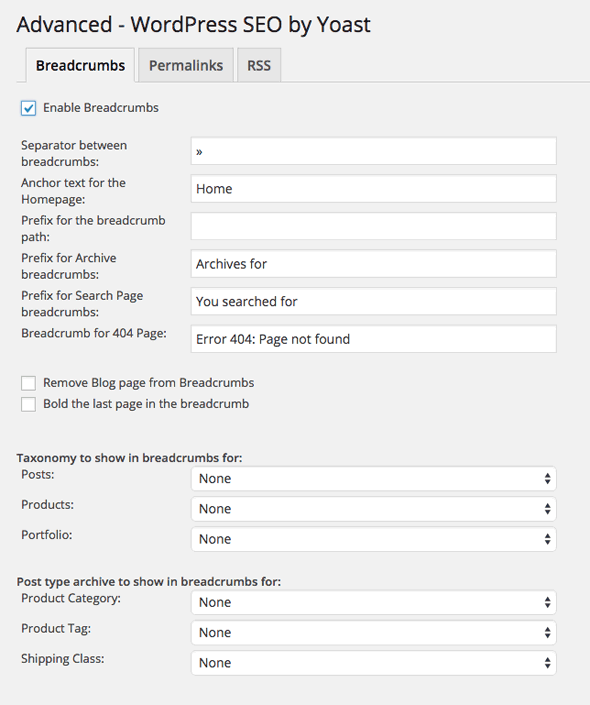
Internal links is all about the breadcrumbs and is a great tool for user navigation and site structure.
Here the separator is the 2 arrows/chevrons ‘>>’ known in html terms as ‘»’ for a different separator here is a list to choose from, use the field value under the ‘Entity Name’ the remainder of the fields are wording and prefixes for the breadcrumbs go with what you like.
For the Taxonomy – choose the structure that is stronger in your site; category or tags.
To set up breadcrumbs you needs to add the php code to your theme:
<?php if ( function_exists('yoast_breadcrumb') ) {
yoast_breadcrumb('<p id="breadcrumbs">','</p>');
} ?>
Copy the code above and paste it into your theme templates. Using WordPress default 2011 theme as an example, pasting the code into the ‘index.php’ after the div with an id of primary like this:
get_header(); ?>
<div id="primary">
<?php if ( function_exists('yoast_breadcrumb') ) {
yoast_breadcrumb('<p id="breadcrumbs">','</p>');
} ?>
<div id="content" role="main">
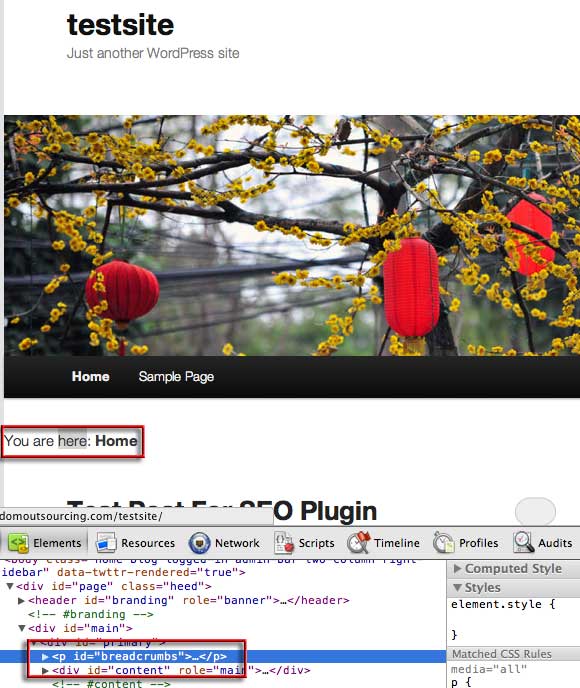
Will result in the placement of the breadcrumb here:
You can place the breadcrumb code anywhere in the template to position it and also in other WordPress templates where you want the breadcrumbs to appear – use the target id of ‘breadcrumbs’ to style it in CSS. If it doesn’t appear at all you most likely need to paste it to another template which your theme is using.
RSS
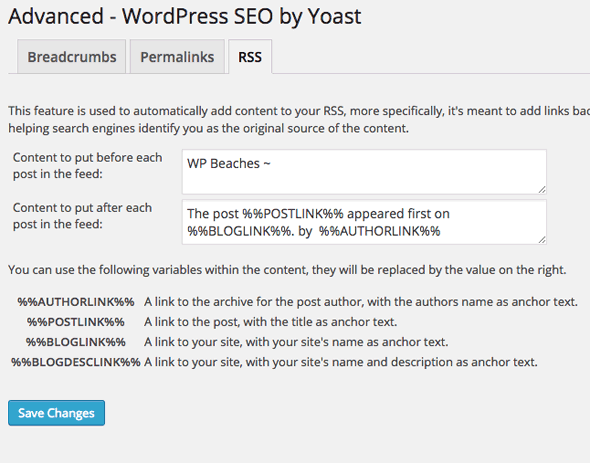
The RSS options here add additional content to your RSS feed which link back to your site – it is used to add more ownership back to your site if your content is republished without your consent as known as scraping. Adding these tags will include links back to your blog before and after each post giving you the benefit of inbound links.
Next up is the Tools menu which controls Import/Export, Bulk Editor, File Editor and a recalculation of posts with a focus keyword.
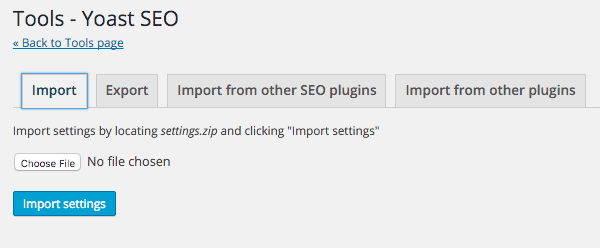
Import & Export
The import/export tools allow you import/export your actual Yoast SEO settings which is great for adding to another site.
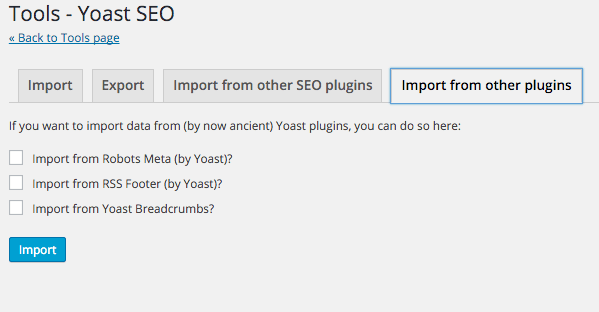
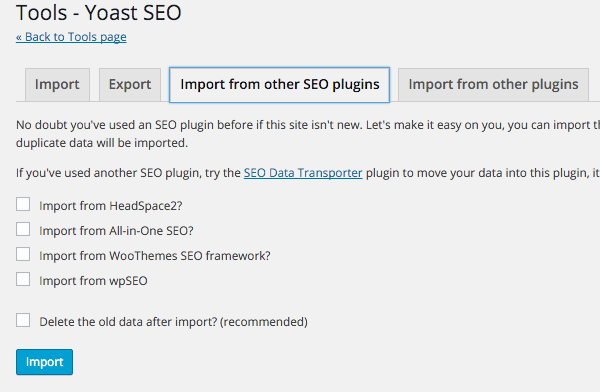
Here you can import from 3 of the other SEO plugins, HeadSpace2, Woo Themes SEO and All-in-One SEO and also import from other Yoast Plugins – Robots/RSS and Breadcrumbs – once you have imported just delete the older plugins.
A great feature here is the export settings which can save a lot of time in setting up another installation, which on the new site you just import which is a huge time save for all the variables set up at a global level.
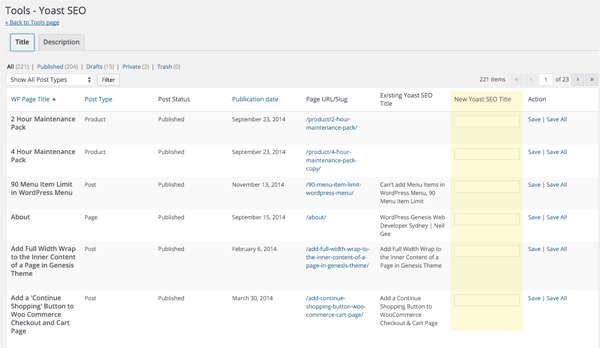
Bulk Title and Description Editor
Here you can bulk edit the title and descriptions of your posts/pages.
Edit Files
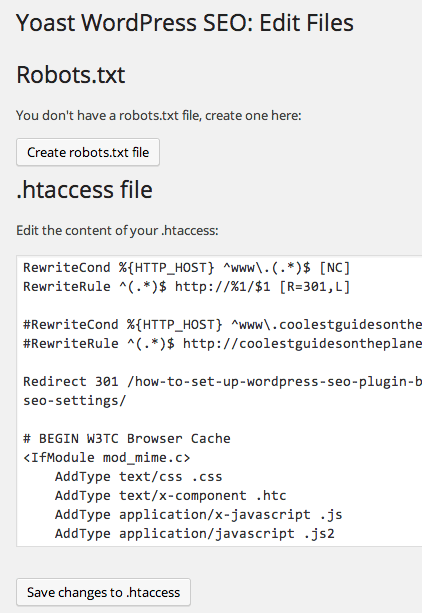
This is handy – straight access to your .htaccess file, also if you have a robots.txt in your root level this will also be editable in this screen.
Extensions
Here you can buy and manage some additional premium SEO extensions.
Search Console
If you have authenticated to Googles Search Console you can see and mark as fixed any 4o4 pages.
Local SEO Box Options
The local WordPress SEO settings appear on each Post and Page, settings divided in 3 vertical tabs; general, advanced and social settings.
Category and Tags also have a local settings but are limited to the regular tags and SEO options.
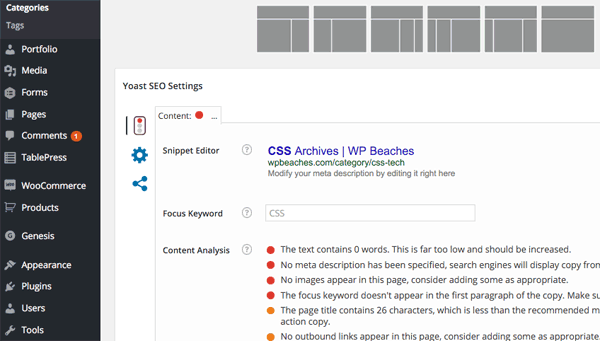
General
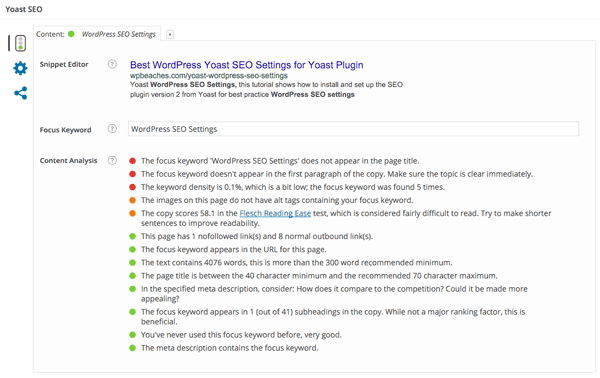
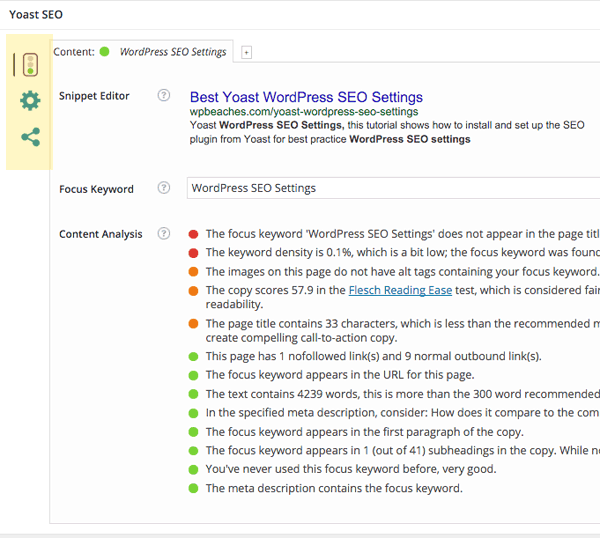
In the general tab, you can see a snippet preview of how the post/page would look in a Google search results listing page , you can add in your title, description and keywords What is most powerful is the focus keyword which when you add one and update your content it will alert you to the various places that keyword phrase needs to be used, don’t get too obsessed with all the options having green lights – for example in the above example the words ‘WordPress SEO Settings’ are in the page title yet the content analysis says it isn’t.
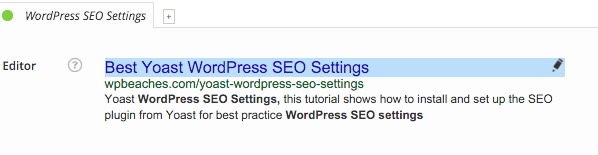
To edit the title, URL and description – just hover over the field, click the pencil and edit away.
Since I have added my own values here the global settings will be overridden.
Content Analysis
Content analysis info will give you some pointers for better SEO work on the post/page – look at the analysis and make sure you have a decent amount of green balls, yellows are not the end of the world but avoid the reds. The content analysis has been developed in real time so you don’t have to save to see improvements to the scores.
Focus Keyword Reminders
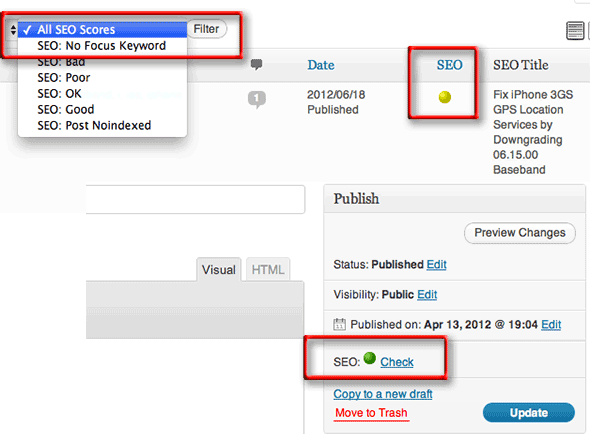
focus-keyword-analysis
In the new version of this plugin are a bunch of interface reminders to check and use the focus keyword functionality, you will see these in the post/page edit screens as well as in the ‘all posts’ and ‘all pages’ listing screens. Set the focus keyword and let the plugin tell you what you need to do to optimise the content for it.
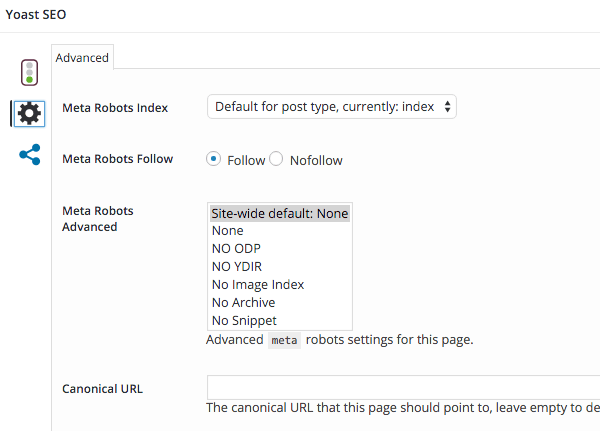
Advanced
The advanced tab has a suite of powerful options – the defaults are perfect.
If you need to set redirects, canonicals, noindex or nofollow for specific content then this is the place.
Social
You can overwrite the default titles and descriptions and images in your content that will be displayed when your links are posted in Facebook , Twitter and Google Plus. This would override the page title, meta description and featured image.
Category/Tags/Taxonomies – Local Settings
In categories and tags and custom taxonomies you can also overwrite the global settings with the above fields per category (or tag), these are accessible when you edit the category or tag or custom taxonomy.
Summary
This plugin should be in your top 5 list of needed plugins for WordPress, the author really knows his stuff and I believe it will be very hard to top this in terms of SEO for WordPress. There is a lot of settings which have also been done for you under the hood which conform to Google’s best practices, look for upgrades to the plugin when they become available and always update to the latest version.
This latest version has had a lot of backend code optimisation, so the plugin will load faster than previous, and is set to load only the features it requires per content displayed.
SEO wise this will really prepare your site for full optimization when dealing with all search engines, it doesn’t mean you’ll start ranking No.1 in Google for any old phrase but rather gives you a solid foundation on which you need to build and develop quality rich content.